Uraan Pakistan: The Five-Year National Economic Plan 2024-29

- 102
- 0
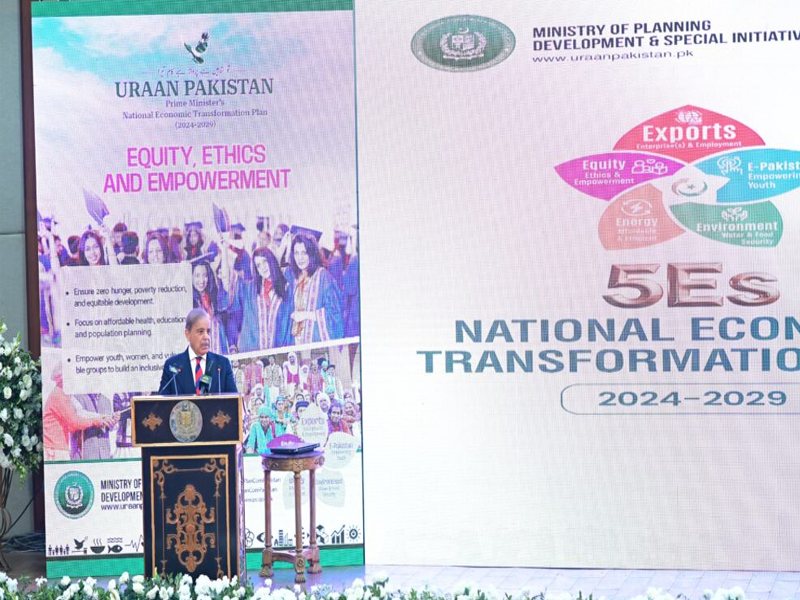
On December 31, 2024, Prime Minister Shehbaz Sharif's government launched the much-anticipated Uraan Pakistan: Home-grown National Economic Plan 2024-29, a comprehensive blueprint aimed at revitalizing Pakistan's economy over the next five years.
This bold initiative is structured around five core pillars, known as the 5Es Framework-Exports, E-Pakistan, Environment, Energy & Infrastructure, and Equity, Ethics & Empowerment. By focusing on these key areas, the government seeks to position Pakistan as a competitive player in the global economy while also working to improve the quality of life for all its citizens. Vision and Goals of the Uraan Pakistan Plan The overarching vision of the Uraan Pakistan plan is to transform the country's economic landscape through sustainable growth, macroeconomic stability, and the empowerment of local industries. According to the Ministry of Planning, the plan was crafted with input from both public and private sectors, reflecting a broad consensus on the priorities for Pakistan's development. The goals set forth by the government include achieving a sustainable GDP growth rate of 6% by 2028, creating one million jobs annually, and attracting $10 billion in private investment every year. Core Pillars of the Plan 1. Exports The first pillar of the Uraan Pakistan plan focuses on significantly boosting exports.
With Pakistan's exports remaining stagnant in recent years, the government aims to identify new markets, promote local industries, and increase the value-added component of exported goods. Prime Minister Shehbaz Sharif emphasized that export-led growth is the "only option" to make Pakistan's economy stronger. In pursuit of this objective, the government will work to streamline export processes, provide incentives to exporters, and reduce barriers to trade. The plan includes a targeted export growth of up to $60 billion by 2028. A key aspect of this will be the diversification of Pakistan's export portfolio, moving away from traditional sectors such as textiles and raw commodities, to include more technology and high-value products. Additionally, Pakistan will work to foster partnerships with regional and global trade partners, particularly in the Middle East, Europe, and Asia. 2. E-Pakistan The second pillar, E-Pakistan, focuses on the digital transformation of the country. As part of the plan, the government seeks to create an enabling environment for digital businesses, promote innovation, and enhance Pakistan's digital infrastructure. With the rise of the digital economy, this pillar aims to turn Pakistan into a hub for digital services, e-commerce, and tech innovation.
A critical component of E-Pakistan is the expansion of high-speed internet connectivity to rural and underserved areas. By improving access to the internet, the government hopes to stimulate entrepreneurial activity, create jobs, and boost productivity in various sectors. The plan also includes initiatives to develop Pakistan's information technology (IT) and fintech industries, which have shown great potential in recent years. In the long run, E-Pakistan aims to modernize education, healthcare, and government services through digital platforms, ensuring that every Pakistani benefits from the advantages of a connected world. 3. Environment and Climate Change Given the growing threat of climate change and Pakistan's vulnerability to environmental challenges, the third pillar of the Uraan Pakistan plan emphasizes the importance of sustainability. The government aims to enhance efforts in addressing environmental degradation, promoting renewable energy, and building resilient infrastructure to cope with climate-related risks. One of the key elements of this pillar is the transition to clean, renewable energy sources, particularly solar, wind, and hydropower. Pakistan aims to reduce its dependence on fossil fuels and lower carbon emissions while meeting the increasing energy demand of the country. The government will also invest in large-scale afforestation projects to combat deforestation, which has contributed to severe flooding and landslides in various parts of the country. Additionally, Pakistan will work to implement climate-smart agriculture practices, which will help improve food security while mitigating environmental impact. The government has committed to making sustainable development a priority and has set ambitious targets for green growth.
4. Energy and Infrastructure The fourth pillar focuses on addressing the country's energy and infrastructure challenges, which are key drivers of economic growth. Pakistan's energy sector has faced persistent issues of inefficiency, high costs, and shortages. The government aims to modernize the energy infrastructure, improve electricity transmission systems, and reduce energy losses, which have been a major drain on the economy. Through investments in renewable energy, the Uraan Pakistan plan intends to ensure that the country can meet its growing energy demands sustainably. This includes the development of large-scale renewable energy projects, improving energy storage capabilities, and promoting energy efficiency in industry and homes. In addition to energy, the government plans to overhaul Pakistan's infrastructure, focusing on transportation, housing, and water management.
The development of modern transport networks, including rail and road systems, is critical for ensuring smoother trade flows and enhancing connectivity within the country. Investment in water infrastructure, including the construction of dams and irrigation systems, is essential to improve agricultural productivity and safeguard the country's water resources. 5. Equity, Ethics & Empowerment The final pillar of the Uraan Pakistan plan is Equity, Ethics & Empowerment. This pillar is focused on fostering inclusive growth by reducing poverty, addressing income inequality, and empowering marginalized communities. The government will prioritize policies that promote social justice, ensure equal opportunities for all, and uplift women, youth, and rural populations. Particular attention will be given to improving healthcare, education, and skills training, ensuring that all citizens, regardless of their socio-economic status, have access to the tools and opportunities they need to succeed. The plan also includes measures to tackle corruption, improve governance, and ensure transparency at all levels of government. The government recognizes that economic growth must be inclusive to be sustainable. Therefore, the empowerment of local businesses, especially small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), is central to the plan. By creating a more equitable economic environment, the Uraan Pakistan plan aims to raise the standard of living for all citizens. The Uraan Pakistan: Home-grown National Economic Plan 2024-29 represents a comprehensive and ambitious strategy to address Pakistan's economic challenges and position the country as a competitive player in the global market. Through the 5Es Framework, the government aims to drive growth, innovation, and inclusivity, while ensuring environmental sustainability and economic stability.
As the plan unfolds over the next five years, the government will need to work closely with both the public and private sectors to overcome challenges and achieve the set goals. However, if successfully implemented, Uraan Pakistan has the potential to transform the country's economic landscape, creating a more prosperous and resilient Pakistan for future generations.