Unraveling human trafficking: understanding the causes

- 158
- 0
Human trafficking, a global scourge, remains one of the most heinous crimes, exploiting vulnerable individuals for profit and depriving them of their basic rights and dignity. Behind this multifaceted phenomenon lie a myriad of interconnected factors that drive traffickers to prey on their victims. In this article, we delve into the complex web of reasons behind human trafficking, shedding light on the root causes and contributing factors.
Economic Vulnerability: Poverty and economic hardship are among the primary drivers of human trafficking. Individuals living in poverty, particularly in developing countries, are more susceptible to exploitation due to their desperate circumstances. Lack of education, limited job opportunities, and financial instability compel many to seek employment abroad, often falling victim to traffickers who promise lucrative jobs but deliver exploitation and abuse instead.
Demand for Cheap Labor and Sexual Services: The insatiable demand for cheap labor and sexual services fuels the perpetuation of human trafficking networks. Industries such as agriculture, construction, manufacturing, and domestic work often rely on cheap or forced labor to maximize profits. Similarly, the global sex trade thrives on the exploitation of vulnerable individuals, with traffickers exploiting women, men, and children for commercial sexual exploitation.
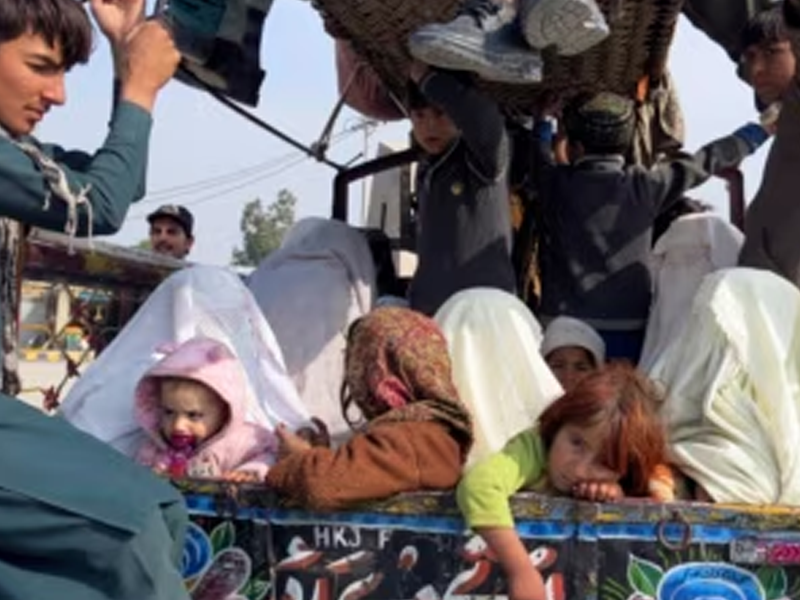
Social and Political Instability: Regions affected by conflict, political turmoil, and social unrest provide fertile ground for human trafficking to flourish. Displacement, disruption of social structures, breakdown of law and order, and weak governance create environments conducive to exploitation and trafficking. In such contexts, vulnerable populations, including refugees, internally displaced persons, and marginalized communities, are at heightened risk of falling prey to traffickers.
Gender Inequality and Discrimination: Gender inequality and discrimination exacerbate the vulnerability of women and girls to trafficking. Patriarchal societies, entrenched gender norms, and limited opportunities for women's education and empowerment perpetuate their exploitation. Women and girls are disproportionately affected by trafficking for sexual exploitation, forced labor, and forced marriage, facing systemic barriers to protection and justice.
Lack of Awareness and Enforcement: Insufficient awareness about the realities of human trafficking and inadequate enforcement of anti-trafficking laws contribute to its prevalence. Many individuals, especially in rural or marginalized communities, lack knowledge about the tactics used by traffickers and their rights as victims. Moreover, corruption, complicity, and weak law enforcement agencies enable traffickers to operate with impunity, hindering efforts to combat trafficking effectively.
Cyber and Technological Advancements: The proliferation of the internet and digital technologies has facilitated new avenues for human trafficking, including online recruitment, grooming, and exploitation. Traffickers exploit social media platforms, online classifieds, and encrypted communication channels to lure victims and evade detection. The anonymity and reach of the internet present challenges for law enforcement and require innovative approaches to combat online trafficking.
Human trafficking is a multifaceted phenomenon rooted in economic, social, political, and cultural factors. Addressing this complex issue requires a comprehensive approach that addresses the root causes while prioritizing victim protection, law enforcement, and international cooperation. By understanding the underlying reasons behind human trafficking, stakeholders can work towards effective prevention strategies, prosecution of traffickers, and support for survivors, ultimately striving towards a world free from exploitation and injustice.
Published in The Daily National Courier, March, 07 2024
Like Business on Facebook, follow @DailyNCourier on Twitter to stay informed and join in the conversation.