The rise of virtual reality: Exploring its impact on society and beyond

- 204
- 0
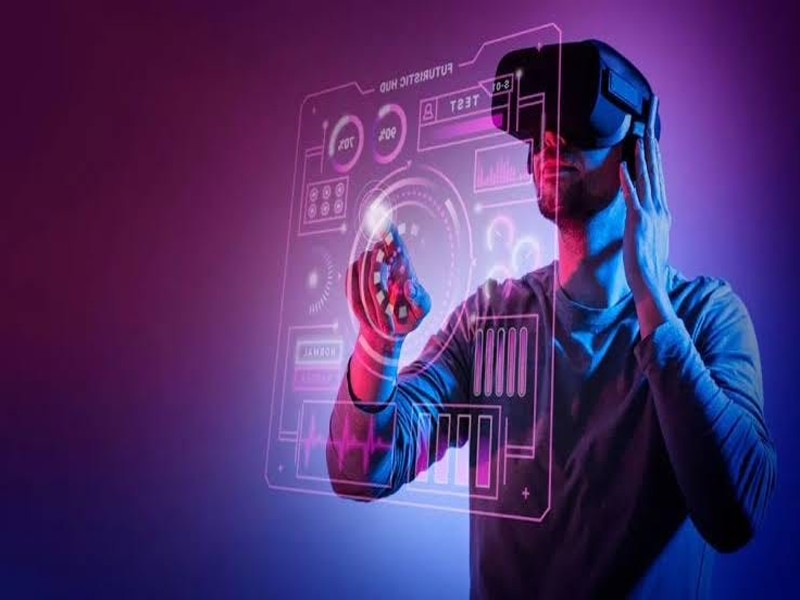
Virtual reality (VR) has emerged from the realm of science fiction to become a transformative technology with profound implications across various facets of society. Initially conceptualized in the mid-20th century, VR gained popularity in the 1980s with rudimentary systems that aimed to simulate artificial environments through bulky headsets and basic graphics.
Since then, rapid advancements in computing power, display technologies, and motion tracking have propelled VR into a new era of realism and accessibility. At the core of every VR experience lies sophisticated hardware and software engineered to transport users into digital realms. Modern VR headsets are equipped with high-resolution displays that provide crisp visuals, precise motion sensors that track movements with accuracy, and advanced optics that create immersive environments. Coupled with spatial audio and haptic feedback devices, these systems engage multiple senses, blurring the lines between physical and virtual realities. Entertainment and gaming have been driving forces behind the mainstream adoption of VR technology.
VR gaming, in particular, has revolutionized interactive entertainment by offering players unprecedented levels of immersion and engagement. Whether exploring fantastical worlds, participating in competitive sports simulations, or solving puzzles in virtual escape rooms, VR gaming has expanded the boundaries of what is possible in interactive media. The ability to physically move within virtual spaces and interact with objects and characters in real-time enhances the sense of presence and agency, making VR games uniquely captivating. Beyond entertainment, VR has found compelling applications in education and training. In fields such as medicine, aerospace, and engineering, VR enables students and professionals to practice skills in realistic virtual environments. Medical students can perform simulated surgeries, astronauts can train for space missions, and engineers can test prototypes-all within safe and controlled settings. These applications not only enhance learning outcomes but also contribute to reducing risks and costs associated with real-world training scenarios. In healthcare, VR is making significant strides by offering therapeutic benefits in pain management, mental health treatment, and rehabilitation. Virtual environments provide patients with immersive experiences that aid in distraction during procedures, help manage chronic pain through biofeedback techniques, and offer exposure therapies for anxiety disorders and phobias. The ability to create customized virtual scenarios tailored to individual needs has opened new avenues for enhancing patient care and improving treatment outcomes.
Moreover, VR is transforming how architects and designers visualize and present their ideas. By creating virtual models of buildings and spaces, architects can walk clients through virtual tours, allowing them to experience designs in a realistic context before construction begins. This not only enhances client understanding and satisfaction but also facilitates collaborative decision-making and reduces the likelihood of costly design errors. Despite its myriad benefits, the widespread adoption of VR raises ethical considerations and societal implications. Issues such as data privacy, virtual addiction, and the potential for dissociation from reality are subjects of ongoing debate. The immersive nature of VR experiences can blur the boundaries between the physical and virtual worlds, leading to concerns about the impact on interpersonal relationships, mental health, and individual well-being. As VR becomes more integrated into daily life and social interactions, it becomes increasingly important to address these challenges responsibly. Looking forward, the future of VR holds promise for continued innovation and expansion across diverse industries. Emerging technologies such as augmented reality (AR) and mixed reality (MR) are pushing the boundaries of what is possible, offering new dimensions of interactive experiences and applications. Projects in development range from virtual tourism and cultural heritage preservation to immersive storytelling and collaborative virtual workspaces, demonstrating the versatility and potential of VR beyond its current applications. In conclusion, virtual reality stands at the forefront of technological advancement, reshaping industries, redefining experiences, and challenging our perceptions of reality itself. Its impact spans entertainment, education, healthcare, and design, offering unprecedented opportunities for innovation and growth.
As VR continues to evolve, navigating its ethical implications and societal impacts will be crucial in harnessing its full potential while ensuring responsible and equitable integration into our lives. By embracing thoughtful exploration and ethical considerations, we can foster a future where virtual reality enhances human experiences and enriches our understanding of the world around us.